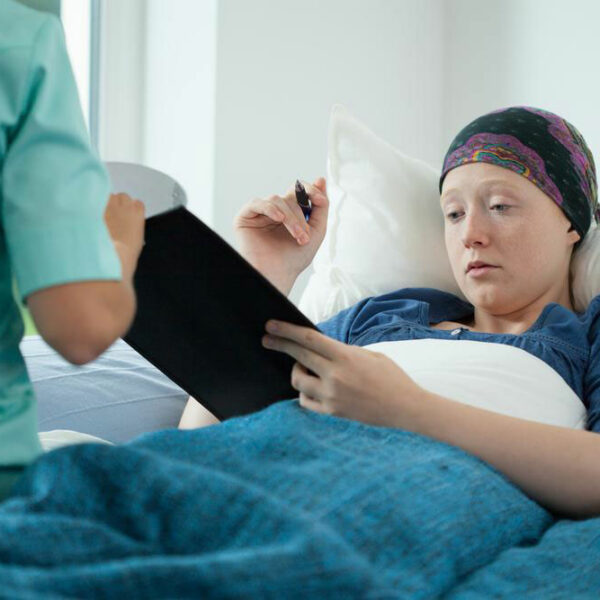
Leukemia, important things to know about symptoms and treatment
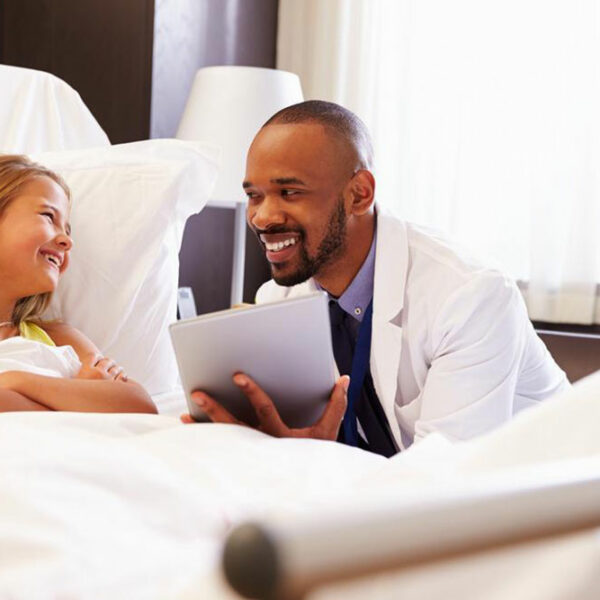
Leukemia means cancer that affects blood cells. Leukemia begins inside the bone marrow, where blood cell production takes place. There are different types of blood cells but leukemia usually targets white blood cells. These white blood cells fight infections. When these cells begin to grow abnormally, it impairs their infection-fighting function. Leukemia can be chronic or acute. Chronic leukemia develops at a slower pace than acute leukemia. Further classification of leukemia is based on the type of blood cells affected by the disease. The leukemia that targets white blood cells (lymphocytes) is called lymphocytic leukemia. Myelogenous leukemia targets red blood cells, granulocytes or platelets. Types of Leukemia Based on different classifications of the disease, there are several types of leukemia. • Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) This is the most commonly-occurring leukemia. It mostly occurs in children but can affect anyone. • Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) This type of leukemia can affect people of all groups but most commonly is seen in adults. • Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) It can develop in adults without manifesting any signs of the disease for long periods of time. • Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) The symptoms may not show for years but then escalate quickly.