What Are The Different Signs And Symptoms Of Kidney Cancer
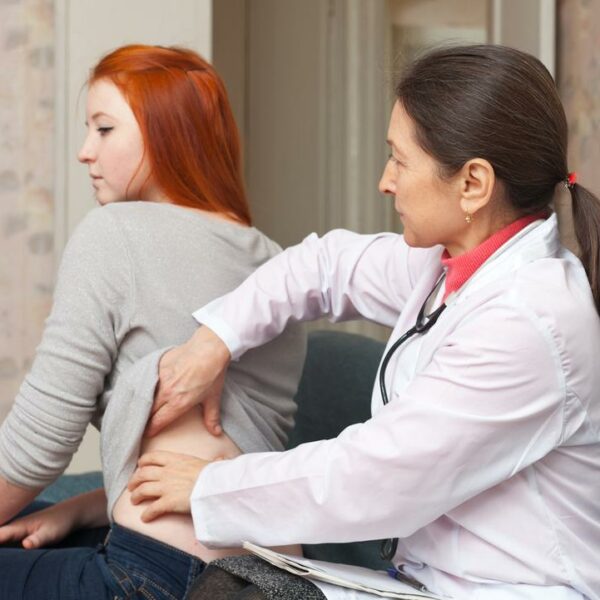
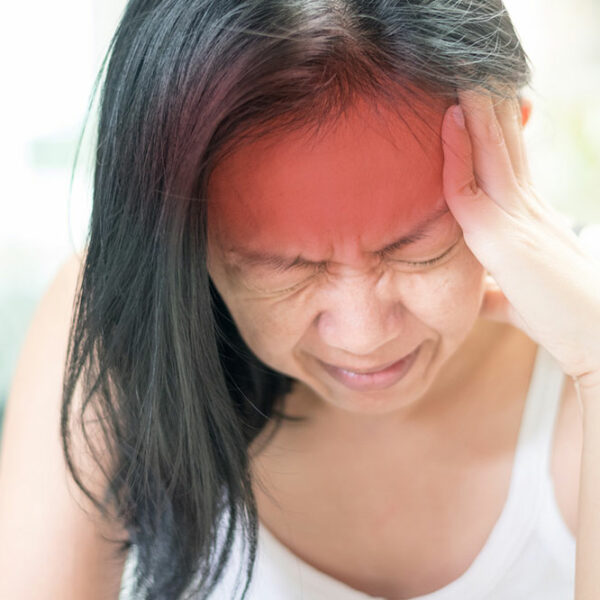
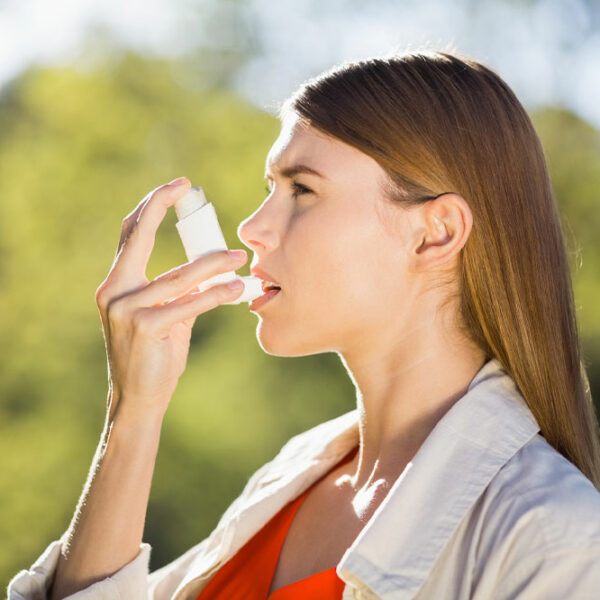
Kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located in the upper abdominal area against the back muscles on both the left and right side of the spine. The major function of this organ is to discharge excess fluid and waste materials from the body through urine. The kidneys also support in controlling the production of red blood cells that help in regulating blood pressure. The pain in the kidney area, i.e., in the back (under the ribs, to the right or left of the spine) is called kidney pain, also known as renal or flank pain. The primary kidney cancer symptoms are an acute and chronic pain, fever, blood in the urine, nausea, and fatigue. Depending on the cause, pain can be felt on both left and right sides or individually and may spread towards the abdomen or groin. The cause of kidney pain may be some underlying diseases that might hamper kidney functioning severely. One of the major causes is kidney cancer. So, the next time when you feel pain in your kidney do not take it lightly as it can be cancerous. Let us know more about kidney cancer and kidney cancer symptoms. Kidney cancer Kidney cancer, also termed as renal cancer is a chronic disease in which kidney cells become malignant and grow out of control, forming a tumor.